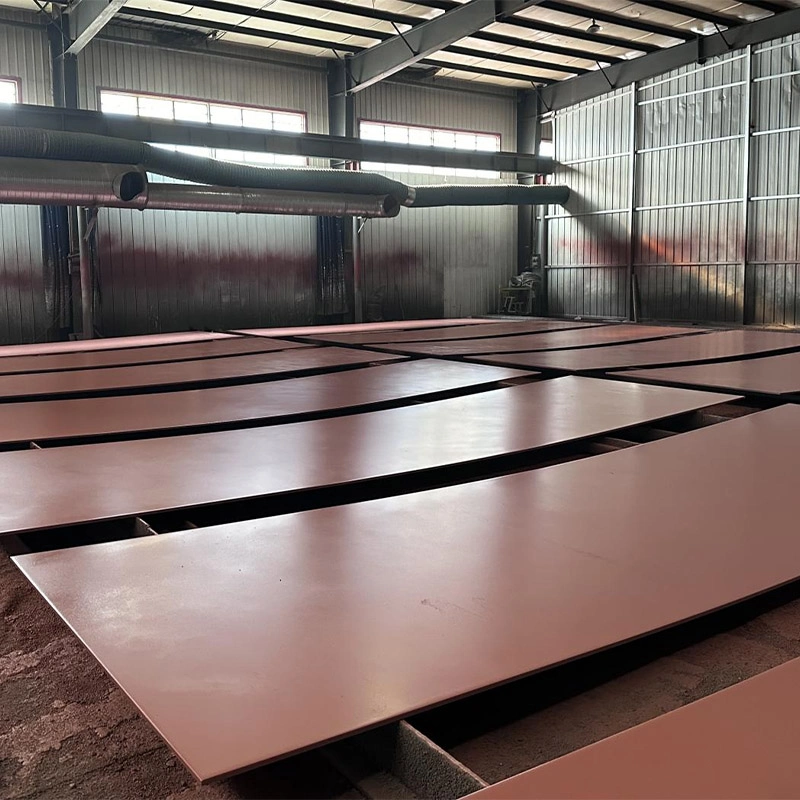
What is A2 Cold Work Tool Steel
A2 Cold Work Tool Steel is a popular cold work tool steel grade. The equivalent Chinese steel grade for A2 is Cr5Mo1V. It is particularly suitable for applications of high hardness, wear resistance, and toughness at room temperature. The working conditions of high-stress steel are harsh, so it requires high hardness, wear resistance, sufficient strength and toughness. A2 tool steel is an ideal middle ground between these characteristics, which is why it is used in many heavily abused and/or abrasive tool applications.
One of the main characteristics of A2 tool steel is its ability to harden in the air, which keeps the distortion to a minimum when heat treating. This characteristic provides dimensional stability and is good for precision components. Besides, its make up has elements which give hardenability and wear resistance thereby proving its significant role under tough and industrial environment.
Chemical Composition of A2 Tool Steel
| Chemical Element | Content | Effect |
| Carbon (C) | 0.95%-1.05% | Provides the necessary hardness and wear resistance. |
| Chromium (Cr) | 4.75%-5.50% | Enhances hardenability and corrosion resistance. |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 1.00%-1.25% | Improves toughness and heat resistance. |
| Vanadium (V) | 0.15%-0.50% | Contributes to wear resistance by forming stable carbides. |
| Manganese(Mn) | ≤1.00% | Improve the microstructure of steel and enhance its performance. |
Cold work tool steel typically contains high carbon content to ensure superior hardness and wear resistance. Alloying elements like Cr, Mo, W, and V are added to improve hardenability and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-wear applications. These elements work synergistically to create a microstructure with tempered martensite or bainite structures distributed with fine carbides, ensuring the material’s durability under extreme conditions.
Physical Properties of A2 Tool Steel
Cold Work Tool Steel possesses characteristics that render it well suited for challenging uses.
- High Wear Resistance:The steels durability is enhanced by the scattering of carbides in its structure, which helps maintain a smooth surface and precise dimensions when subjected to significant friction between the mold and workpiece surfaces thanks to its high hardness (30% 50% greater, than the workpiece) and tempered martensite or bainite formations.
- Thermal Stability:A grade A tool steel is able to maintain its durability and resistance to wear when subjected to high temperatures during the process of machining or shaping materials. This quality of retaining hardness and wear resistance at elevated temperatures is essential for the effectiveness of hot work molds and high speed cutting tools, in industrial applications.
- Ease of Working with Tools:Even though A2 is quite tough, in nature it can be easily worked with if the right techniques are used during production. Tool steel generally allows for processing and can be even better optimized through heat treatment.
The unique characteristics of A2 Cold Work Tool Steel allow it to consistently excel in tool applications, across a wide range of industries.
Mechanical Properties of A2 Tool Steel
The mechanical properties of A2 Cold Work Tool Steel are essential for its functionality in industrial applications:
- High Hardness:The material achieves superior hardness levels after appropriate heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering.
- Exceptional Toughness:Despite its high hardness levels, A2 demonstrates excellent toughness, enabling it to withstand impacts without fracturing easily. Cold work tool steel like DC53 maintains high hardness while offering exceptional toughness, making it suitable for high-impact load applications.
- Strength:Strength is a critical factor in resisting deformation or breakage under stress conditions. Strength, indicated by tensile and compressive yield points, is crucial for mold parts to resist deformation and breakage.
- Fatigue Resistance:For components subjected to repeated impact loads over time, fatigue resistance ensures longevity without failure.
- Gall Resistance:Galling occurs due to “cold welding” between surfaces under frictional contact; A2’s ability to resist galling enhances its performance in forming tools.
- Heat Softening Resistance:The ability to maintain mechanical properties such as hardness under thermal loading makes this material ideal for demanding environments where temperature fluctuations occur frequently.
Each of these mechanical properties contributes significantly to the widespread use of A2 Cold Work Tool Steel in industries ranging from automotive manufacturing to aerospace engineering.
Production Process of A2 Tool Steel
The production process of A2 Cold Work Tool Steel is meticulously designed to optimize its properties for industrial applications. The process involves several critical stages that ensure the steel achieves its desired characteristics, including high hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability.
Forging Process
The forging process plays a pivotal role in improving the internal structure of A2 Tool Steel. Forging reduces machining allowance and steel consumption while improving internal defects like carbide segregation, reducing harmful impurities, and enhancing the steel’s structure. Good forgeability means low hot forging deformation resistance, good plasticity, a wide forging temperature range, and minimal tendency to crack or precipitate network carbides. This step ensures the steel’s microstructure is uniform and free from defects, which is essential for maintaining its mechanical properties during use.
Machinability
A2 Cold Work Tool Steel is known for being challenging to machine due to its high hardness and wear resistance. Cold work tool steel, primarily hypereutectoid and ledeburitic steels, is generally challenging to machine. Proper heat treatment can enhance machinability, while high-surface quality molds may use free-cutting steel containing elements like S and Ca. These measures improve the ease of machining without compromising the material’s performance.
Heat Treatment Process
The heat treatment process plays a role in crafting A Tool Steel as it involves both hardening and tempering to strike the right balance between hardness and toughness needed for its intended use case. Several factors come into play during this process such as hardening capability and resistance to tempering alongside considerations, for overheating sensitivity and oxidation levels. Manufacturers meticulously manage these elements throughout the heat treatment process to customize A Tool Steel according to its designated applications specifications and demands.
Each stage in the production process contributes significantly to the overall quality and performance of A2 Cold Work Tool Steel. From reducing impurities during forging to optimizing machinability through heat treatment techniques, these steps ensure that the steel meets stringent industry standards.
Industry Application of A2 Tool Steel
A2 Cold Work Tool Steel finds extensive applications across various industries due to its exceptional mechanical properties such as high wear resistance, toughness, and dimensional stability at room temperature.
Automotive Industry
In automotive manufacturing processes where precision and durability are critical:
- Stamping Dies:Essential for producing automotive body parts; A2 ensures high precision and durability.
- Cold Heading Dies:Used to manufacture bolts, screws, and rivets critical for vehicle assembly.
- Punches and Dies:Utilized cutting and forming operations for producing small parts with consistent accuracy.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace applications demand materials capable of withstanding extreme conditions:
- Sheet Metal Forming Tools:Utilized in shaping aircraft body parts while ensuring high strength and wear resistance.
- Trimming Dies:For trimming excess material from forged or cast aerospace components with tight tolerances.
- Cold Extrusion Dies:Used in creating high-strength aerospace fasteners with complex shapes.
Construction Industry
In construction-related manufacturing processes:
- Shear Blades:Employed in cutting reinforcement bars or structural steel sheets used in building construction.
- Drawing Dies:For producing wires or cables needed in construction-grade applications with consistent diameter.
- Blanking Dies:Used for cutting shapes from steel sheets required for structural components.
Tool and Die Making Industry
A key sector where precision tooling is indispensable:
- Mold Inserts and Dies:Critical for plastic injection molding or die-casting applications requiring durability.
- Forming Rolls:Employed in roll-forming processes used to produce metal profiles or shapes.
- Thread Rolling Dies: Designed for forming threads on tools or fasteners with accuracy.
Manufacturing Industry
Widely utilized due to its adaptability:
- Cutting Tools:Ideal for manufacturing drills or end mills ensuring longevity under heavy-duty conditions.
- Slitting Cutters:Used for cutting narrow strips from metal sheets efficiently.
- Cold Forging Dies: Suitable for producing high-strength parts with precise dimensions through cold forging processes.
Promispecial® Best Tool Steel Solution
Promispecial® offers advanced tool steel solutions tailored to meet the diverse demands of industries. With a focus on quality and innovation:
- Superior Wear Resistance:Highlighted as a critical property by Promispecial®, tool steels ensure long service life even under frequent frictional or abrasive conditions. Powder metallurgy tool steel (PM) features outstanding wear resistance due to its uniform microstructure and fine carbide distribution.
- Excellent Toughness:Despite achieving high hardness levels required by cold work tool steels such as carbon tool steel or alloy tool steel; Promispecial® ensures exceptional toughness enabling tools crafted from their materials to withstand impacts without fracturing easily.






.webp)