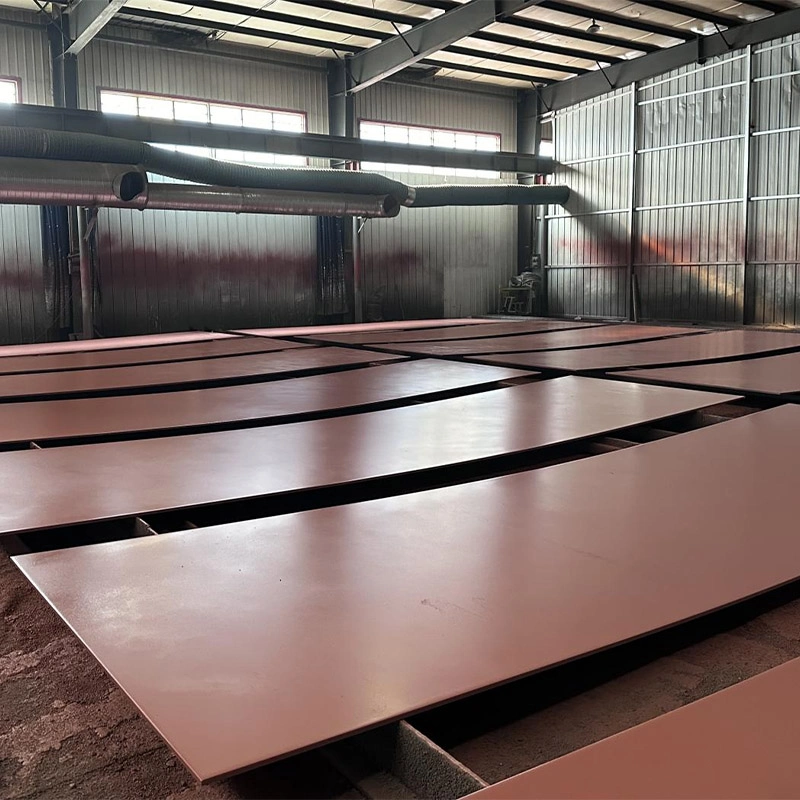
Abrasion resistant steel is extremely useful in different sectors where industrial components should be durable for a duration of time, all other things being equal. Due to its unique characteristics, it is the obvious choice of material for industries that suffer from heavy wear and tear hence saving tons of expensive parts. The use of this ‘clean’ steel is only increasing as manufacturers look to cut costs and improve efficiency by preventing downtime from equipment failure.
Importance of Abrasion Resistant Steel in Industrial Applications
Enhancing Lifespan of Critical Components
A major advantage of including abrasive resistant steel in designs is the longevity it adds to critical components. This steel is used in the building of machines and equipment for excavation, mining, helping them to work efficiently even in such adverse situations. These components have a strong chemical structure and are not as worn down with use, meaning that they function properly more consistently than other materials.
In addition, the wear resistant quality of abrasion resists steel requires less frequent changes — a factor that has positive implications on the environment via reduced manufacturing of new parts. As a result, businesses can ensure the effective utilization of resources, without compromising on operational efficiency.
Reducing Downtime and Maintenance Costs
Another important aspect of abrasion resistant steel is its ability to significantly cut maintenance costs and reduce downtime. Industries that rely on heavy machinery often face challenges related to wear and tear, leading to unexpected equipment failures. By utilizing abrasion resistant steel, companies can mitigate these risks, resulting in fewer disruptions during production.
Longer-lasting components lead to reduced maintenance schedules, enabling businesses to allocate resources toward other project-critical areas. The financial implications of using such steel extend beyond mere saving on replacement costs; improved consistency in production runs can also enhance profitability by ensuring that machinery operates without interruptions.
Chemical Composition and Properties of Abrasion Resistant Steel
Key Alloying Elements
Abrasion resistant steel and its titanium carbide is fundamental to the powerful properties that this specific kind of steel has. Generally, steel this high is carbon based with added alloys like chromium, manganese and molybdenum. These elements give the material superior hardness and wear resistance to fit in high-performance applications.
This is where alloying elements come in to improve steel microstructure and, as a result, the overall performance of the material. For example, chromium helps for greater hardness and corrosion resistance, while manganese contributes to better impact toughness so the material can absorb more energy from hits before it deforms or shatters.
Mechanical Properties Enhancing Durability
The mechanical properties of abrasion resistant steel set it apart from conventional steel. It exhibits enhanced hardness, usually rated between 450 and 600 BHN (Brinell hardness numbers), contributing to its exceptional wear resistance. The steel also possesses good toughness, which, while ensuring that it can endure impact forces, helps prevent structural failure during operation.
Moreover, abrasion resistant steel showcases an impressive fatigue resistance that supports heavy-load applications. This characteristic is crucial in industries where components are regularly subjected to dynamic stresses that could lead to rapid failure in standard materials.
Advantages of Upgrading to Superior Grades of Abrasion Resistant Steel
Resource Efficiency during Production
Upgrading to superior grades of abrasion resistant steel translates to resource efficiency during production. High-grade varieties usually require less raw material compared to lower-grade counterparts, as they are designed to deliver better performance and longevity. Consequently, companies can experience improved yield rates and resource conservation throughout the manufacturing process, which ultimately translates to reduced environmental impact.
Cost Savings in Long-Term Applications
Incorporating superior grades of abrasion resistant steel leads to significant cost savings in long-term applications. Although the initial investment may be higher, the extended lifespan of these materials, coupled with reduced maintenance and replacement costs, ensures lower overall expenditures.
In many cases, businesses discover that upgrading their material choices enhances their bottom line, as they experience fewer machine failures and increased productivity due to minimal operational interruptions. This consolidated approach fosters better resource management and budgeting, positioning organizations for sustained growth.
Environmental Benefits: Reducing Material Consumption Over Time
By adopting higher-grade abrasion resistant steel, industries not only save on costs but also contribute to sustainable practices. A decline in material consumption translates to a reduced carbon footprint associated with manufacturing and transportation processes. Over time, this could lead to substantial reductions in waste and resource depletion, aligning well with global efforts aimed at achieving sustainability.
In summary, the advantages and essential role of abrasion resistant steel in industrial applications cannot be overstated. By enhancing the lifespan of critical components, reducing downtime, and providing financial and environmental benefits, this type of steel, such as Promispecisl’s abrasion resistant steel plate, stands as a significant asset for industries striving to maintain competitive advantages in a challenging environment.
Innovations in Abrasion Resistant Steel Technology
Recent Advances in Metallurgical Processes
Metallurgy has come along way, offering how we make abrasion resistant steel in an entirely different light. Its physical and mechanical properties became easier for its performance to be enhanced under difficult conditions through the application of modern techniques. Technologies like more higly-tailored alloy compositions and specialized manufacturing processes are employed to create steels with exactly the properties that industry requires.
This steel is now also manufactured using methods such as controlled cooling and specific tailored heat treatment protocols. The performance properties of abrasion resistant steel can be improved by implementing the proper cooling rates during solidification, manufacturers say. These improvements increase the lifecycle of the material and provide a much higher service level than is possible with normal steels, which would fail in many applications.
Heat Treatment Techniques Improving Hardness and Toughness
Heat treatment is central to maximizing the hardness and toughness of abrasion resistant steel, and recent innovations have refined these techniques. The process typically involves heating the steel to elevated temperatures followed by rapid quenching, which can vastly improve its hardness. However, it’s the subsequent tempering process that plays a crucial role in ensuring that while the steel is hard, it retains the necessary toughness to resist cracking and deformation.
Advanced tempering procedures, such as double tempering or using precise temperature controls, enhance the overall ductility of abrasion resistant steel. This balance is necessary because a material that is too hard without adequate toughness is prone to premature failure under stress. By applying these refined techniques, manufacturers ensure that the resulting steel maintains optimal hardness levels while being resilient to impacts and thermal stresses.
Practical Tips for Using Abrasion Resistant Steel
Proper Storage and Handling
When working with abrasion resistant steel, proper storage and handling practices are essential for maintaining its integrity and performance. It is critical to store the materials in a clean, dry environment free from moisture to prevent rust and corrosion, which can compromise the steel’s inherent durability. If possible, materials should be stored off the ground and elevated to protect them from potential contaminants and environmental factors.
Moreover, during transportation and handling, care should be taken to avoid impacts that could cause dents or scratches on the surface. Using appropriate lifting equipment, straps, and protective padding enhances the safety and preserves the quality of the steel. Work environments should also be organized to minimize unnecessary movements and handling, reducing the risk of material damage.
Essential Maintenance Practices
Maintaining abrasion resistant steel components is vital for ensuring their longevity and performance over time. Regular inspections should be carried out to monitor wear and potential damage, addressing issues before they can lead to more significant failures. This proactive approach can help identify wear patterns that may indicate underlying problems with the application or design, allowing for adjustments to minimize future degradation.
Another significant aspect of maintenance is keeping the components free from debris and abrasive particles that could accelerate wear. Regular cleaning schedules and inspections should incorporate checks for dirt, dust, and other materials that may impair the functionality of the equipment. Implementing these essential maintenance practices minimizes unexpected downtimes and enhances the overall efficiency of operations that rely on abrasion resistant steel components.
In conclusion, the advancements in abrasion resistant steel—stemming from metallurgical innovations and refined handling processes—play a pivotal role in improving the lifespan of materials. By understanding and implementing best practices in storage, handling, and maintenance, industries can harness the full potential of abrasion resistant steel and sustain a competitive edge in their respective fields. Promispecial continuously improves manufacturing and engineering practice processes, keeps producing higher quality and cost-effective steel products, such as tool steel and spring steel, contributing to the rise of China’s steel brand image.






.webp)