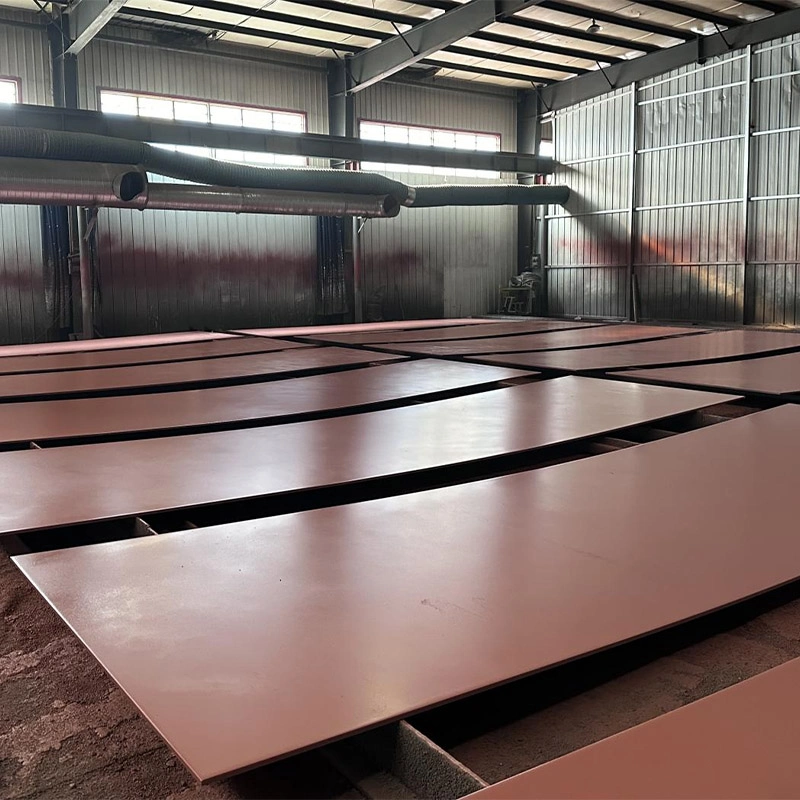
Overview of High-Manganese Austenitic Steels
Austenitic steels with manganese content are considered a type of sturdy steel that is resistant to abrasions and known for its remarkable toughness and ability to harden under work conditions effectively. The steels like Mn12 and Mn13 are renowned, for their capacity to endure impacts and wear and are well-suited for challenging industrial uses.
| Steel Grade | Yield Strength (MPa) |
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
Elongation (A50%) |
Brinell Hardness (HBW) |
Available Specification (mm) |
| Mn13 | ≥300 (471) | ≥700 (1010) | ≥24 (45) | ≥170 (210) | 3.0~25.0× 1000~2050 |
| X120Mn12 | ≥300 (465) | ≥700 (1020) | ≥20 (41) | ≥170 (220) | 3.0~25.0× 1000~2050 |
| Mn12 | ≥300 (475) | ≥700 (1020) | ≥20 (42) | ≥170 (220) | 3.0~25.0× 1000~2050 |
Characteristics of High-Manganese Austenitic Steels
Chemical Composition
Manganese austenic steels usually have a substantial amount of manganese content that often goes beyond 10%. This element plays a role, in maintaining the austenitic phase at normal temperature levels effectively ensuring the durability and flexibility of the steel while also providing notable work-hardening characteristics.
Mechanical Properties
Manganese austenitic steels have outstanding tensile strength and ductility properties that make them stand out in terms of mechanical characteristics. When subjected to impact or extrusion forces these steels demonstrate notable work hardening on their surfaces. The stressed surface undergoes work hardening resulting in an increase in surface hardness from an initial HB200 level to over HB750 all the while preserving excellent impact toughness, at the core.
Historical Development and Applications
Evolution in Steelmaking
The creation of manganese austenitic steels has been motivated by the necessity for materials that can withstand harsh environments while maintaining efficiency intact. Over the years progress in steelmaking methods has enabled regulation, over the substance makeup and microscopic structure of these steels which in turn has improved their resistance to wear and longevity.
Common Industrial Uses
Rich austenitic steels see extensive use in sectors like mining equipment and machinery production due to their durability in high wear and high impact settings like those found in shot blasting tools and large jaw crushers—a testament to their adaptability, in multiple industries.
Metallurgical Features of Mn12 and Mn13 Steels
Microstructure Analysis
Austenite Stability
The durability of the austenite phase in Mn12 and Mn13 plays a role in how well they perform. The significant presence of manganese helps maintain the stability of austinite when under pressure. This allows for work hardening without shifting to less resilient phases such, as martensite.
Grain Structure
The strength of Mn12 and Mn13 steels is enhanced by their grain structure which aids in evenly dispersing stress across the material and decreasing the chances of crack formation when under load.
Impact of Manganese Content on Properties
Wear Resistance
These steels have increased wear resistance due to the manganese content they contain. Abrasion-resistant steel is known for its hardness that gives it superb resistance against wear and impact; thus making it ideal, for tough conditions where durability is key.
Toughness and Ductility
Even though Mn12 and Mn13 are known for being materials, with high strength and hardness properties they also possess good low-temperature impact resistance which guarantees consistent performance in various environmental settings.
Processing Techniques for High-Manganese Austenitic Steels
Heat Treatment Processes
Annealing Techniques
Annealing is used to reduce tensions, in high manganese austenic steels to enhance their ease of machining while preserving their natural durability characteristics. It is important to apply annealing methods to achieve the ideal combination of strength and flexibility in the steel product.
Quenching and Tempering
Enhancing the properties of these steels can be achieved through quench and temper methods that enable controlled transformation of microstructures, for better wear resistance while maintaining toughness.
Fabrication Methods
Welding Considerations
When working with manganese austenitic steels it’s important to handle the welding process carefully because of their special characteristics. The goal is to maintain control during welding to avoid grain growth or a decrease in ductibility, at the weld point.
Machining Challenges
Working with these materials can be tricky because of their toughness but, by using the right tools and methods it’s possible to make accurate cuts without harming the material itself. Even though abrasion-resistant steel is hard to work with it can still be cut, welded, and machined effectively with the tools and techniques.
In conclusion, steels with a manganese content such as Mn12 and Mn13 provide significant benefits in terms of durability, strength, and versatility across different sectors. Their special mix of ingredients, physical characteristics, metallurgical attributes, and manufacturing methods make them essential for use in situations requiring toughness, in harsh environments.
Comparative Analysis with Other Steel Grades
Advantages Over Conventional Steels
Manganese austenitic steels have numerous benefits compared to standard steel grades because of their remarkable toughness and ability to harden when worked with—giving them an edge over traditional materials in settings where impact and wear are common occurrences. They’re known for their durability and can lengthen the lifespan of components by reducing maintenance expenses and downtime. Additionally, the unique feature of these steels is their capacity to retain ductility at high hardness levels, a blend of properties that sets them apart, from other steel varieties.
Limitations and Challenges
While manganese austenitic steels offer many benefits they also come with some drawbacks and obstacles to overcome. One significant hurdle is their nature, which can make them challenging to work with. Although these steels are resistant to wear and tear they may not be the suitable option, for tasks that demand precise execution or involve intricate shapes. Cutting through abrasion steel requires specialized tools and skills but with the right equipment and know how it can be welded and machined effectively.
Exploring Promispecial® Abrasion Resistant Steel
Promispecial® abrasion-resistant steel is a development in the realm of durable materials that resist wear and tear effectively. This specialized steel excels in conditions by delivering top-notch wear resistance while maintaining strength and flexibility without any compromise in quality or durability; it’s no wonder why Promispecial® range of wear-resistant steel is a popular choice in industry applications like mining, construction, and heavy machinery production.
In today’s industry landscape manganese austenitic steels such as Mn12 and Mn13 remain crucial for their distinct properties that are ideal for tough environments. Their capability to withstand impacts, combat corrosion, and endure harsh conditions makes them vital materials for applications requiring exceptional resilience, in extreme situations.







.webp)