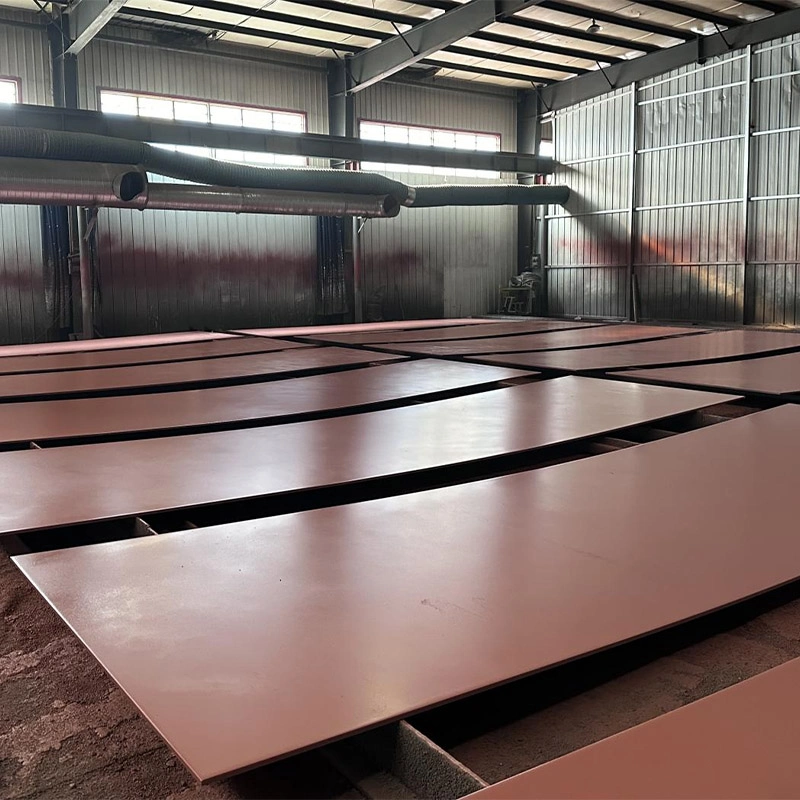
Overview of Free Cutting Steel
Definition and Characteristics
Free cutting steel, also called machinable steel, is a kind of alloy steel whose machinability is improved by adding certain elements in it. Free-cutting steel, more commonly called machinable steel, is a type of alloy steel that has been designed to enhance its machinability through the addition of sulfur, phosphorus, and lead. This type of steel is mainly used in the manufacture of precision mechanical parts that require a high degree of automation and accuracy.
Basic Chemical Composition
Basically, free cutting steel is an addition of elements like sulfur, phosphorus, lead, calcium, selenium, tellurium, and bismuth.
- Sulfur Free-Cutting Steel:Provides improved machinability due to the formation of manganese sulfide. However, excess sulfur impairs mechanical properties.
- Lead Free-Cutting Steel:Lead acts as a lubricant during cutting and does not affect the mechanical properties of the steel at room temperature.
- Calcium Free-Cutting Steel:Calcium forms low melting point oxides that act as lubricants during high-speed machining.
- Selenium, Tellurium, and Bismuth Free-Cutting Steel:These elements significantly improve the machinability but may reduce slightly the ductility and toughness of the steel.
Key Properties and Features
Free cutting steel has great machinability that reduces tool wear, and production efficiency and tool life are greatly improved. Machinability: The best machinability for free cutting steel results in less tool wear and greatly improved production efficiency and tool life. Besides that, it offers good electroplating performance for replacing copper products cost-effectively. Surface Finish: The surface finish of workpieces made out of free-cutting steel is high. Environmental Compliance: It is in line with EU SGS environmental certification, and it can be exported with various mechanical equipment.
Production Process
Manufacturing Techniques
The manufacturing techniques for free cutting steel involve processes like gas cutting, plasma cutting, and punch cutting for shaping the materials into desired forms.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control measures are crucial in ensuring that free cutting steel meets specific standards. Before cutting, remove rust, oil, and other debris on the surface of the steel plate to ensure cutting quality. After cutting, the oxide scale and sulfur residue on the cutting surface should be removed and transferred to the following process. Cutting tolerances and quality should meet the “Construction Specifications.”
Exploring Free Cutting Steel Grades
| Free Cutting Steel | ||||
| NO. | GB | ASTM/AISI | DIN | JIS |
| 1 | Y12/Y12Pb | 12L14 | 9SMnPb28 | SUM24L |
| 2 | Y15/T15Pb | 12L14 | 9SMnPb36 | SUM23 |
| 3 | Y20 | 1213/1215 | 10S20 | SUM32 |
| 4 | Y30 | 1132/1144 | 11SMn30 | SUM43 |
| 5 | Y35 | 1137 | 11SMn37 | SUM43 |
| 6 | Y40Mn | 1141 | 11SMnPb37 | SUM42 |
| 7 | Y45Ca | SUM41 | ||
Common Grades and Their Applications
Free cutting steels are classified based on their chemical composition which determines their grades. These grades are utilized across various industries including automatic lathes, electronics, home appliances, and office equipment for manufacturing gears, shafts, bolts, and standard components like watch components and eyeglass frames.
Differences Between Grades
The differences between grades arise from their chemical composition which affects their mechanical properties such as ductility and toughness.
Selection Criteria for Specific Uses
Selection criteria for specific uses depend on factors like required machinability level, and mechanical properties needed for application-specific tasks such as tensile strength or hardness.
Mechanical Properties of Various Grades
Tensile Strength and Hardness
The tensile strength and hardness of different free-cutting steel grades vary depending on their chemical composition which influences these mechanical properties.
Machinability and Surface Finish
Different grades offer varying levels of machinability which impacts production efficiency while maintaining a high-quality surface finish.
Advantages of Using Free Cutting Steel
Enhanced Machinability
Impact on Production Efficiency
The enhanced machinability of free-cutting steels leads to increased production efficiency by allowing faster processing times with minimal tool wear.
Reduction in Tool Wear and Tear
Using free-cutting steels reduces tool wear significantly thereby extending tool life during manufacturing processes.
Cost-Effectiveness
Material Savings
Cost-effectiveness is achieved through material savings due to reduced waste during machining operations enabled by improved precision offered by these steels.
Time Efficiency in Manufacturing
Time efficiency is another advantage provided by free-cutting steels as they allow quicker turnaround times in manufacturing cycles thus optimizing overall productivity.
Application Fields of Free Cutting Steel
Automotive Industry Applications
The high-quality and more precise nature of free cutting steel, together with great machinability, makes it irreplaceable within this branch. Free-cutting steel provides reliability for the creation of important items that must withstand high volumes of automation processing: gears, shafts, and bolts. These materials are necessary for various lines of industry to make gears, shafts, bolts, and standard parts by turning processes; for this reason, it is not possible to refuse automotive applications either. It can reduce tool wear and increase production efficiency, allowing manufacturers to meet the demanding standards of the automotive sector.
Electronics and Electrical Applications
In the realm of electronics and electrical engineering, free cutting steel is utilized for producing components that demand high precision and surface finish. Specific products include watch components, eyeglass frames, electronic terminal pins, and carburetors. The material’s excellent electroplating properties provide a cost-effective alternative to copper products while ensuring environmental compliance with EU SGS standards. This makes free cutting steel an ideal choice for intricate parts found in electronic devices and electrical equipment.
Promispecial® Products and Applications
Free Cutting Steel Solutions
Promispecial® offers tailored free cutting steel solutions to cater to diverse industrial needs. By leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques such as gas cutting, plasma cutting, and punch cutting, Promispecial® ensures that our products meet stringent quality control measures. Before cutting, remove rust, oil, and other debris on the surface of the steel plate to ensure cutting quality. These processes are meticulously managed to deliver high-quality free cutting steel solutions that align with industry-specific requirements.
Industry-Specific Applications
Promispecial® provides industry-specific applications by offering customized free cutting steel grades that meet unique demands across sectors. Whether it’s enhancing machinability for automatic lathes or ensuring durability in home appliances and office equipment, Promispecial® adapts its offerings to suit varied applications. The workpieces made from free-cutting steel have a high surface finish, which is critical for industries requiring aesthetic appeal alongside functionality.
By understanding the nuances of free cutting steel grades and their applications across different fields, professionals can make informed decisions about material selection for their projects. This knowledge not only aids in optimizing production processes but also contributes to achieving superior product quality and performance in respective industries.






.webp)